Social media has become integral to our daily lives, connecting us with friends, family, and the world. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat offer endless opportunities for sharing moments, ideas, and experiences.
However, while social media brings people closer together, it also has a significant impact on our mental health.
The constant barrage of posts likes, and comments can sometimes leave us feeling overwhelmed or inadequate. The pressure to present a perfect image online can lead to feelings of insecurity and self-doubt.
Several studies have shown that excessive use of social media can contribute to anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues, especially among young people.
Usage Of Social Media
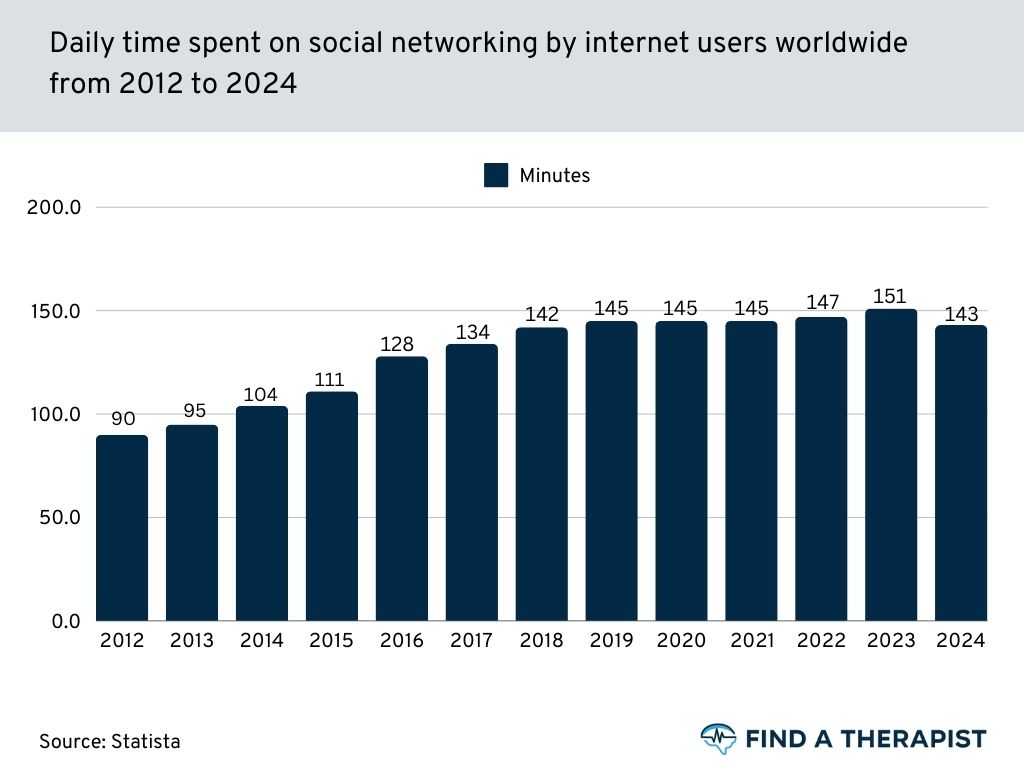
143 Minutes
per day spent daily on social media
(Source)
According to Statista, as of 2024, the average daily social media usage among internet users worldwide was 143 minutes, down from 151 minutes in the previous year.
Brazil ranks the highest in daily social media consumption, with online users spending an average of three hours and 49 minutes per day, while the United States averages two hours and 16 minutes daily, as reported by Statista. (source)
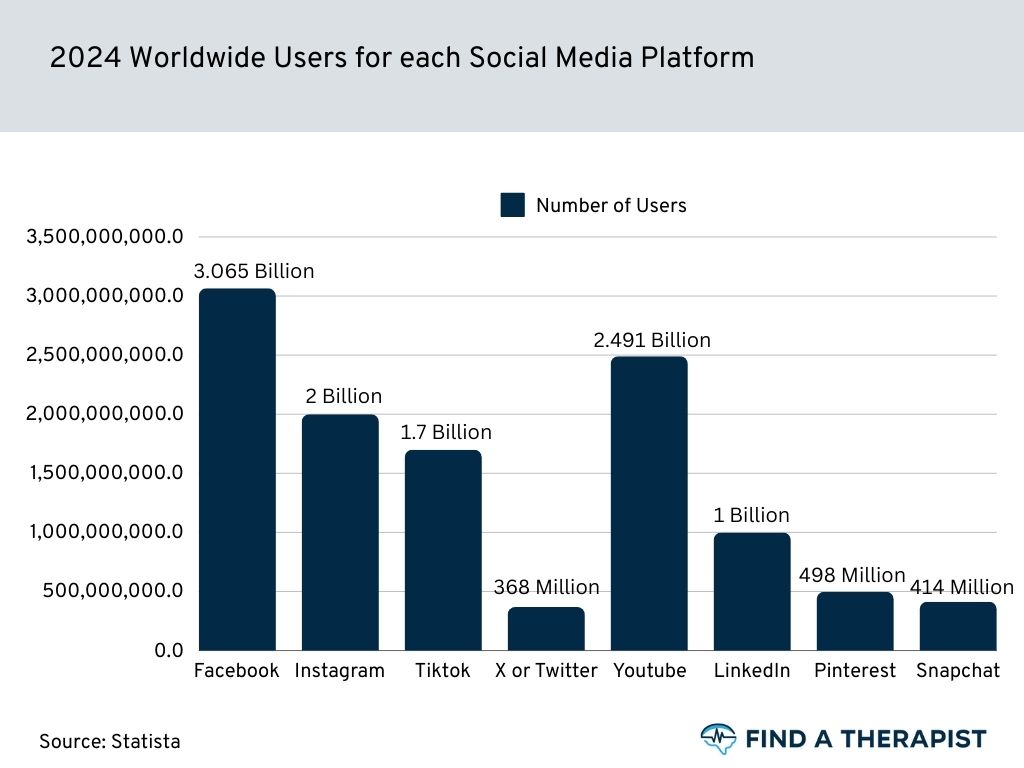
3.065 Billion
uses facebook
(Source)
Facebook boasts an impressive user base of over 3.065 billion individuals, making it one of the most widely used social media platforms globally. With its diverse range of features and functionalities.
Facebook continues to serve as a prominent hub for connecting people, sharing content, and engaging in various online activities. Its immense popularity highlights the platform’s enduring relevance in the digital landscape. (source)
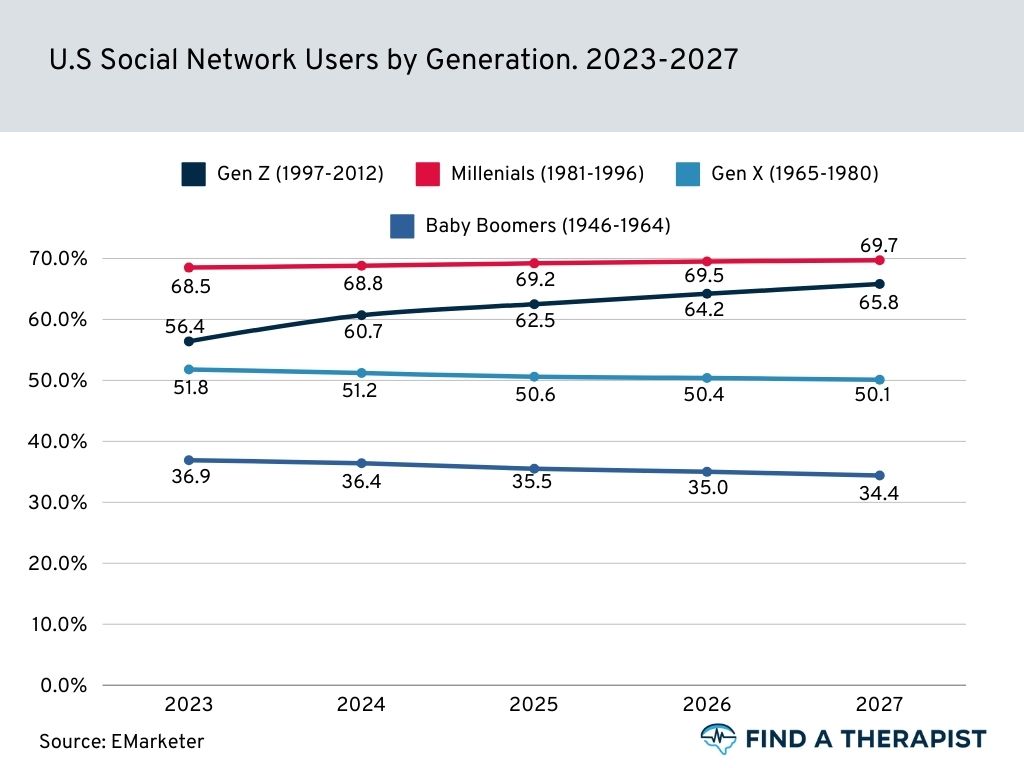
68.8% of Millenials
are active on social media
(Source)
Millennials, often regarded as the first generation to fully embrace social media, maintain a significant presence on various digital platforms, with a remarkable 68.8% actively engaging in social media activities.
From sharing personal updates to participating in online discussions and consuming content.
Millennials demonstrate a profound integration of social media into their daily lives, reflecting the generation’s reliance on digital communication and networking. (source)
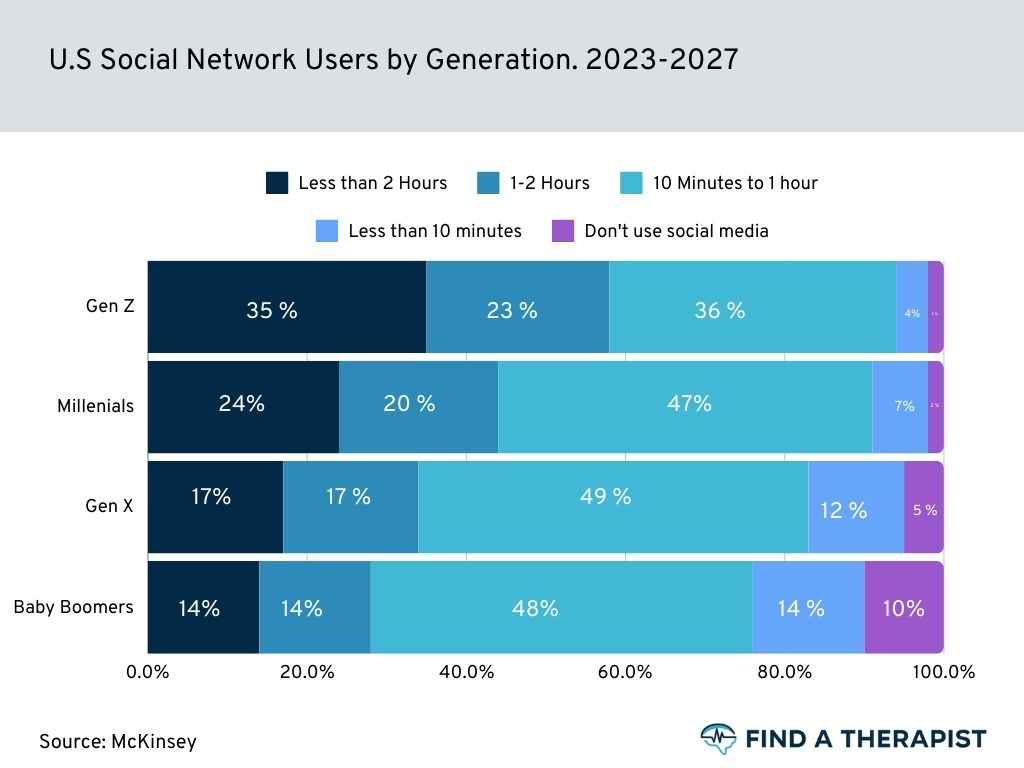
35% Of Gen Z
uses social media for more than 2 hours a day
The younger demographic, Generation Z, exhibits a notable propensity for spending extensive amounts of time on social media, with 35% of individuals from this cohort dedicating more than two hours daily to these digital platforms.
For Gen Z, social media serves as a primary avenue for socialization, self-expression, and information consumption, shaping their worldview and social interactions.
This statistic underscores the profound influence of social media on the behaviors and preferences of the newest generation of digital natives. (source)
Prevalence of Mental Health Issues
The extensive usage of social media platforms has raised concerns regarding its impact on mental health.
Research indicates a significant correlation between excessive social media consumption and various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
As social media continues to evolve and permeate various aspects of daily life, understanding and addressing its impact on mental well-being are crucial for promoting healthier digital habits and fostering psychological resilience.
210 Million
people worldwide suffer from social media addiction
Shockingly, an estimated 210 million individuals worldwide are gripped by social media addiction.
This widespread issue highlights the profound impact of digital platforms on human behavior and mental health.
As society grapples with the consequences of excessive screen time and online engagement, it becomes increasingly crucial to raise awareness and develop strategies to address social media addiction and promote healthier digital habits. (source)
52%
increase in adolescent depression
Over the past decade, there has been a notable increase in mental health concerns, and a recently published national survey suggests that the proliferation of digital media might be a contributing factor.
Twenge’s study, based on data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health, reveals a marked increase in depressive symptoms, psychological distress, and suicidal thoughts among those born in 1995 or later, known as iGen.
Notably, this surge in negative psychological symptoms coincided with the proliferation of social media around 2011.
Twenge suggests that digital media may play a pivotal role in exacerbating mental health disorders among teens and young adults, as opposed to older generations with more stable social lives.
The findings underscore the urgent need for further research into how digital communication, as opposed to face-to-face interactions, influences mood disorders and suicidal tendencies.
65%
surge in suicide rates for girls
The suicide rate for girls has surged by 65%, coinciding with the rise of smartphone use and increased engagement on platforms like Instagram and TikTok.
While it’s crucial to acknowledge that correlation does not imply causation, the evidence suggesting a connection between excessive social media consumption and depression demands our attention.
Studies indicate a significant uptick in depressive symptoms among adolescents, paralleling the widespread adoption of smartphones. (source)
22.6%
suffered from anxiety
In a study conducted among a nationally representative sample of Chinese citizens during the pandemic, 22.6% of participants were found to suffer from anxiety due to frequent social media exposure.
This alarming statistic underscores the profound effects of excessive social media consumption on mental well-being, particularly during times of crisis.
As society grapples with the challenges of the digital age, addressing the detrimental effects of social media on anxiety levels becomes increasingly imperative for promoting holistic mental health support. (source)
Other Impacts of Social Media
Beyond the surface, social media can harbor detrimental effects on mental health, self-esteem, and overall well-being, particularly among young people.
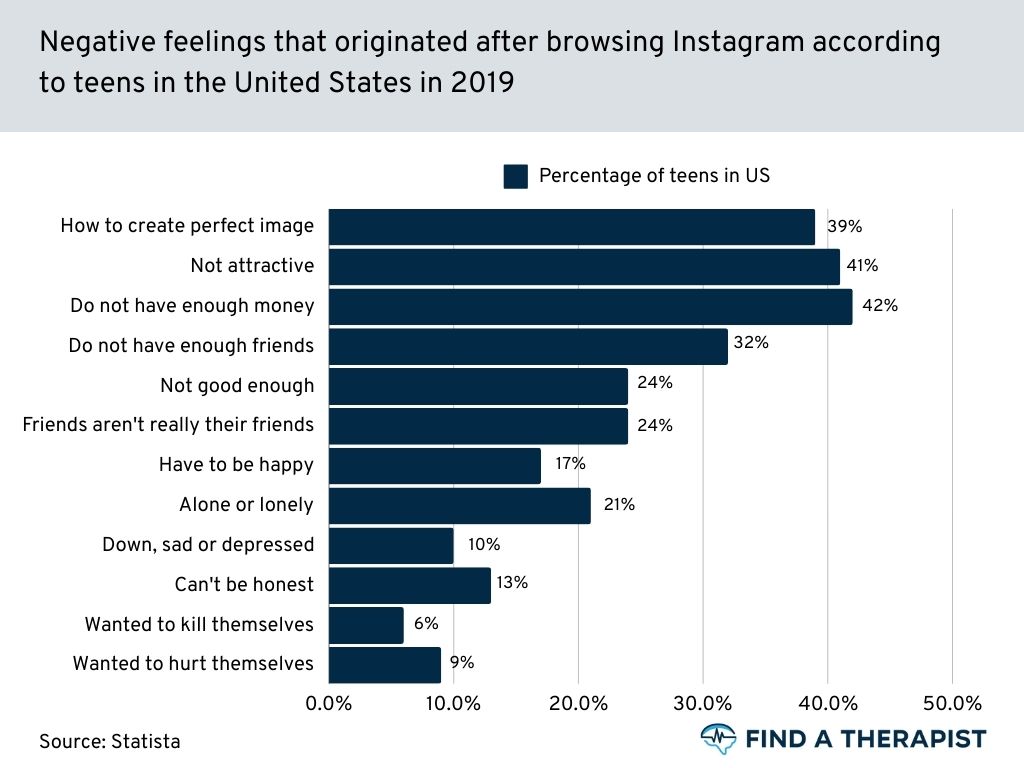
43%
of young people said that they felt they were not attractive
(Source)
With platforms saturated with carefully curated images and unrealistic beauty standards, it’s easy for users to compare themselves unfavorably to others.
The constant barrage of flawless photos and filtered lifestyles can breed feelings of inadequacy and self-doubt, fueling a relentless pursuit of unattainable perfection. (source)
42%
felt they did not have enough money
Similarly, 42 percent of young people feel they don’t have enough money, influenced by the conspicuous consumption showcased on social media.
The glamorization of material possessions and extravagant lifestyles can create a sense of financial inadequacy, leading to dissatisfaction with one’s circumstances and fostering a culture of relentless consumerism. (source)
15%
had encountered sexualized images
Another concerning aspect of social media’s impact is the exposure to sexualized images, affecting 15 percent of young users.
The internet’s vast landscape harbors explicit content that can easily infiltrate feeds and timelines, exposing unsuspecting individuals, particularly adolescents, to inappropriate material.
This premature exposure not only distorts perceptions of healthy relationships and sexuality but also poses risks to mental and emotional well-being. (source)
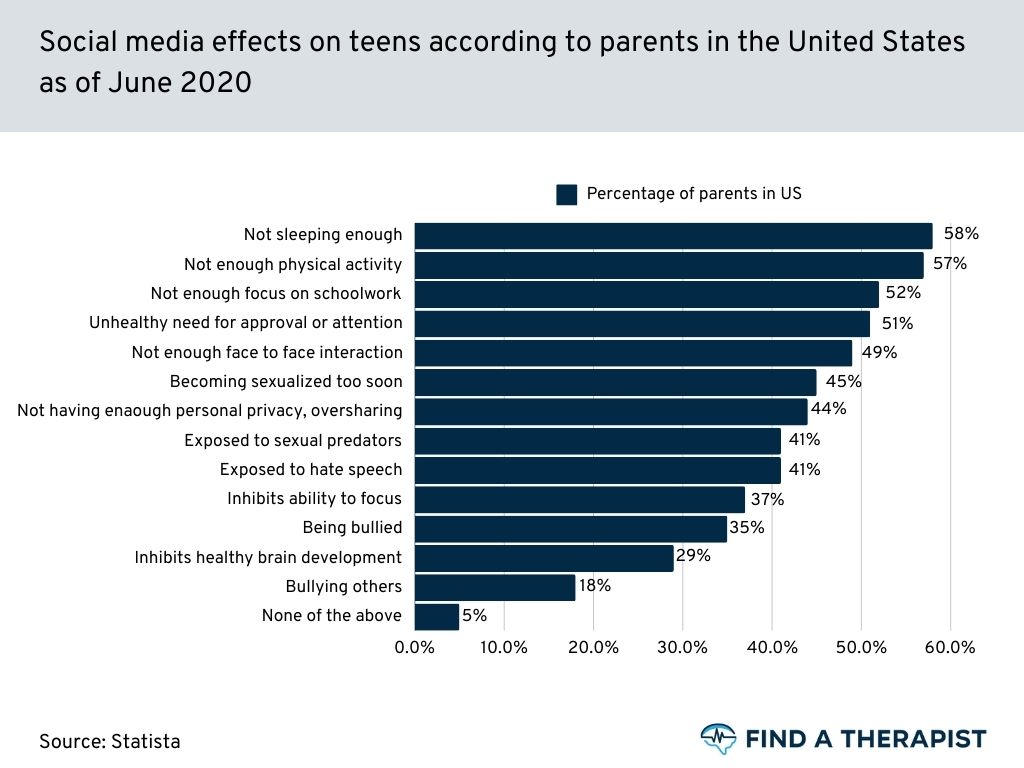
58%
said that it caused them to not sleep enough
The pervasive nature of social media also disrupts sleep patterns, with 58 percent of parents reporting that their children had inadequate sleep due to its influence.
The constant stream of notifications, the allure of endless scrolling, and the pressure to stay connected contribute to a culture of sleep deprivation.
This chronic lack of sleep not only impairs cognitive function and academic performance but also exacerbates mental health issues, such as anxiety and depression. (source)
30 Minutes
per day of social media can lead to increased mental health benefits
Despite these negative impacts, research suggests that limited and mindful use of social media can offer mental health benefits.
Spending just 30 minutes per day engaging with positive and meaningful content can foster a sense of connection, boost self-esteem, and reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Setting boundaries, such as turning off notifications or designating specific times for social media usage, can help individuals strike a healthy balance between online engagement and real-life experiences. (source)
Conclusion
While social media undeniably fosters connectivity and community engagement, its adverse effects on mental health cannot be overlooked.
By understanding the statistics and concerns surrounding social media usage, individuals can make informed decisions about their online habits and prioritize their mental well-being in the digital realm.
As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of social media, it’s imperative to foster a healthy balance between virtual interactions and real-life experiences for a happier, more fulfilling existence.